FAQ – Questions and answers about fire protection coatings
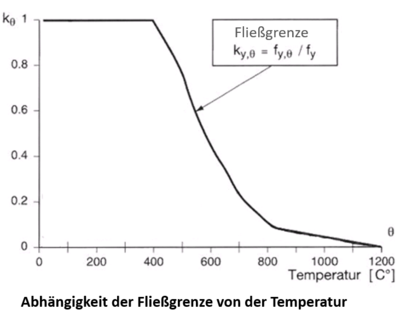
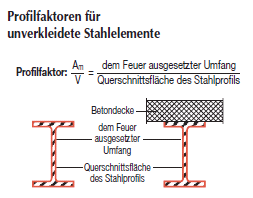
Zunehmende Erwärmung im Brandfall führt zu einer Reduzierung des Tragverhaltens von Stahlbauteilen. Beim Erreichen der kritischen Stahltemperatur besteht die Gefahr des Versagens, d. h. der Verlust der Tragfähigkeit tritt ein. Durch Brandschutzbeschichtungen wird der Zeitpunkt bis zum Erreichen der kritischen Temperatur so lange wie möglich bzw. so lange wie nötig verlängert. Die Beschichtungen schäumen bei Hitzeeinwirkung (ab ca. 200°C) auf und bilden einen isolierenden Kohlenstoffschaum. Die durch den Einsatz von Dämmschichtbildnern maximal erreichbare Feuerwiderstandsdauer richtet sich unter anderem nach der zugrundegelegten Norm: Die oben genannten Bedingungen sind produktabhängig. Den Angaben der Hersteller ist Folge zu leisten. Eine genelle Aussage hierzu ist nicht möglich. Die Hersteller geben Auskunft darüber, ob Systeme mit oder ohne Decklack zugelassen sind. Zur Erlangung der bauaufsichtlichen Zulassung für Dämmschichtbildner für den Außenbereich werden Freibewitterungen von beschichteten Stahlplatten gefordert. Ausgelagerte Platten werden nach 2, 5 und 10 Jahren erneut amtlich geprüft und die Zulassung dann entsprechend verlängert. Das System ist immer mit den von den jeweiligen Herstellern vorgeschriebenen Decklacken zu versehen. Der Profilfaktor ist definiert als Verhältnis des beflammten Umfangs zur Querschnittsfläche des Profils. Für die üblicherweise verwendeten genormten Profile sind entsprechende Tabellen vorhanden. Dünnwandige Profile mit entsprechend großem Profilfaktor erwärmen sich rascher und benötigen deshalb größere Schichtdicken des Dämmschichtbildners mit entsprechend besserer Wärmedämmung. Dies erforderliche Schichtdicke ist von mehreren Faktoren abhängig. Hierzu gehören unter anderem: Da eine mechanische Beschädigung weitestgehend ausgeschlossen werden kann, ist eine Wartung nicht erforderlich, sofern kein Wasserschaden auftritt.
E Allgemeine Fragen zu Brandschutzbeschichtungen
E Fragen zum Einsatz von Brandschutzbeschichtungen
E Fragen zur Applikation von Brandschutzbeschichtungen
E Fragen zur Bemessung von Dämmschichtbildnern
E Fragen zur Pflege und Wartung von Brandschutzbeschichtungen
